On February 25, 2021, the National Dental Examining Board of Canada (NDEB) announced significant changes to the Canadian dental equivalency process. This article has been updated to reflect those changes.
Becoming an accredited dentist in Canada is no easy feat. The road to practicing dentistry is an intricate, ever-evolving, yet rewarding process that requires highly specialized training and professional development.
For internationally trained dentists seeking to practice dentistry in Canada, the rewards for getting through the examination process and obtaining your license are tremendous as Canada now ranks in the top five countries in the world to practice dentistry in terms of salary and quality of professional life. First-year associates in Canada start with salaries around $150,000 CAD, and the earning potential for senior associates and clinic owners is vast.
Currently, there are three routes available that lead to becoming a dentist in Canada. One option is to attend a Canadian university as an undergraduate. If you are an internationally-trained dentist, you can navigate the NDEB process or take the university route by applying to a bridging program.
Let’s explore each route in further detail.
Pursuing a Dental Degree:
Admission and application requirements for dental school vary from one institution to another. It is important to contact the respective dental school admissions office to determine the specific admission requirements needed. As part of the admissions process, most Canadian dental schools require applicants to provide Dental Aptitude Test (DAT) scores administered by the Canadian Dental Association (CDA).
Luckily, Canada is home to a variety of prestigious dental schools across the country that prospective students can choose from. These include:
– University of Alberta (School of Dentistry)
– University of British Columbia (Faculty of Dentistry)
– University of Manitoba (Faculty of Dentistry)
– Dalhousie University (Faculty of Dentistry)
– University of Toronto (Faculty of Dentistry)
– The University of Western Ontario (School of Dentistry)
– McGill University (Faculty of Dentistry)
– Université de Montréal (Faculté de médecine dentaire)
– Université Laval (Faculté de médecine dentaire)
– University of Saskatchewan (College of Dentistry)
On average, the cost of obtaining a four-year undergraduate dental degree can vary from $50,000 to $200,000 CAD for domestic students and up to $360,000 CAD for international students. Tuition fees typically include both academic, non-academic, and dental instrument fees. However, tuition fees vary for universities, so it is best to do your research before filling out an application.
It’s important to note that registration for the DAT is not an application to dental schools but a step towards getting your foot in the door. Don’t be afraid to schedule a call with an advisor and find out what they’re looking for in successful candidates, such as extracurriculars.
The National Dental Examining Board of Canada (NDEB):
To begin the process with the National Dental Examining Board of Canada (NDEB), you must apply to be accepted into the Canadian Dentistry Equivalency Process. As long as you have a recognized degree, you should be accepted. Due to COVID-19, response times may vary on acceptances as there may be delays to the application process.
Once accepted, the first exam you will need to complete is the AFK (Assessment of Fundamental Knowledge). After you pass this exam, you have two options: you may continue the equivalency process and then take Assessment of Clinical Judgment (ACJ) followed by Assessment of Clinical Skills (ACS), or you may apply to a Canadian university and fulfill a two-year bridging program (more on this option below).
Currently, candidates are allowed three attempts each to pass the AFK and ACJ examinations. Beginning in 2022, however, examinees may attempt the ACS an unlimited number of times within a five-year period.
If you are successful in the equivalency process, you will then need to take the board exams (OSCE & Written) to get your licence to start practicing in Canada. These exams are a requirement to practice dentistry in Canada for all accredited candidates and Canadian university dental graduates.
The NDEB equivalency process costs approximately $50,000 CAD, including course and exam fees. This amount may increase depending on how many attempts you need to pass. Here is a typical breakdown of the costs to expect when navigating the Canadian NDEB equivalency process:
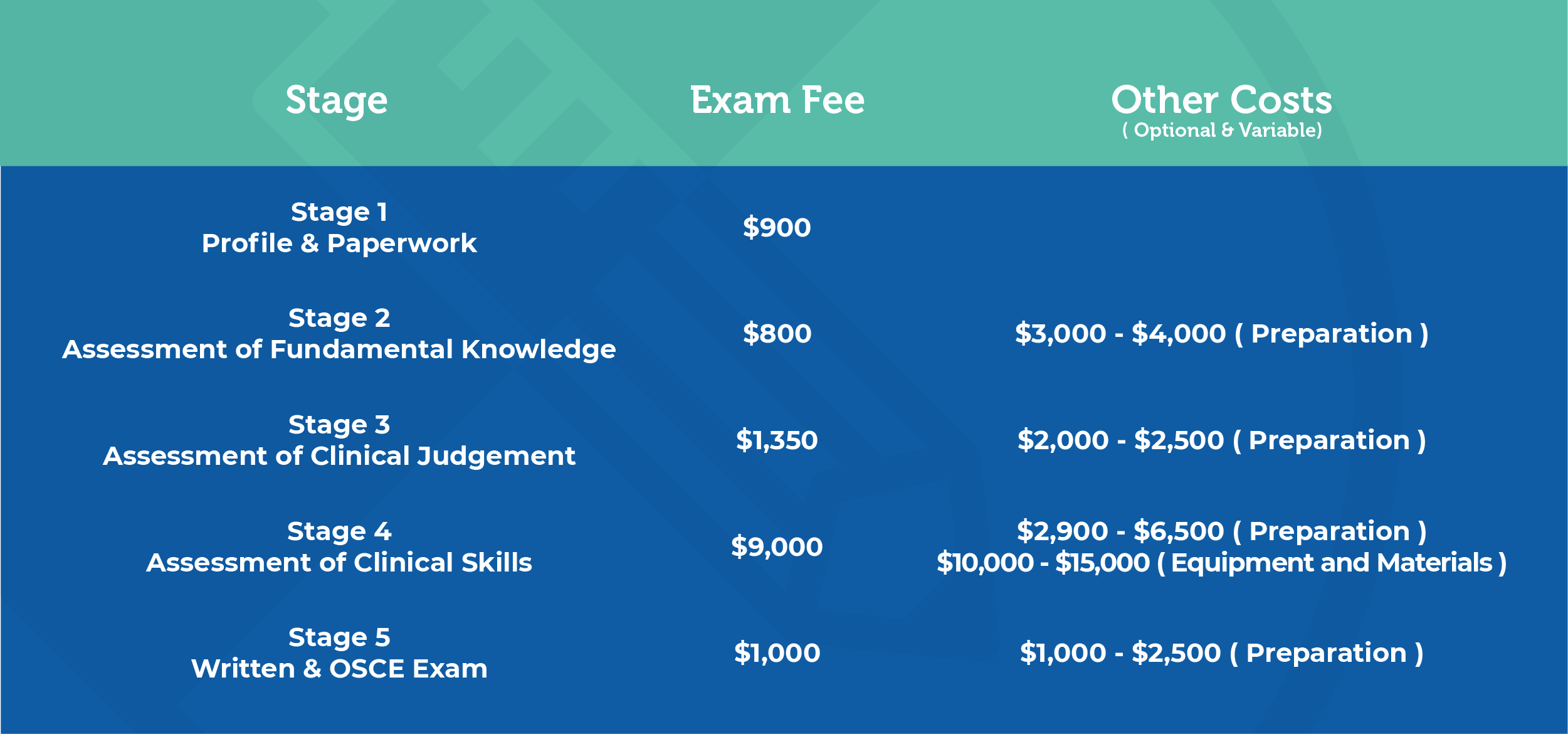
*All prices are in Canadian dollars and reflect the fees as of April 2021. For the latest updates on NDEB exam fees, please visit the NDEB’s website.
In addition to exam fees, you will need to purchase materials (i.e. kits and reusable teeth) to practice dental procedures and techniques. It is also your responsibility to be fully equipped with all the required materials for the actual exam.
At Prep Doctors, we provide specialized dental equivalency courses to help students prepare for each exam administered by the NDEB. Our classes consist of various materials and components, such as comprehensive mock exams, detailed textbooks, and extensive lectures. Find out more about our courses, including registration dates, below:
OSCE & Written Training Course
Bridging Programs:
As we mentioned above, following the completion of the NDEB’s AFK exam, you have the option to enroll in a specialized bridging program offered by Canadian universities. These programs are designed to bridge the gap between international and Canadian dental training.
Bridging programs are held over five to six months, and after successful completion of the program, students can enroll directly into the third year of a four-year Doctor of Dental Surgery Program (DDS). Overall, a DDS degree program can take 2 to 2.5 years to complete.
If you’re looking to take a bridging course, there are some general qualifications that most Canadian universities require:
- You must have completed a minimum four-year University dental program not recognized by the Commission on Dental Accreditation of Canada (CDAC).
- You must have a relatively strong GPA (each university has its own GPA standard).
- Be a Canadian citizen or have permanent residency status in Canada.
- Provide proof of your English abilities. Students whose first language is not English may be required to write the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL), and the Test of Written English (TWE), or equivalent.
- Complete the NDEB’s AFK exam with a high score (preferably 90% or more will greatly improve your chances of acceptance).
If you meet all the requirements for your chosen institution’s program, you will be contacted for an interview or to participate in a bench test.
It is important to note that not every university offers a bridging program. It is best to contact the institution of your choice to confirm its specified entry requirements.
The bridging program process can cost up to $90,000 CAD, but this price may vary depending on tuition fees as well as each institution’s non-refundable application fee.
At Prep Doctors, we also provide courses that help prepare trainees for Canadian universities’ admission bench tests and interviews. Our courses offer trainees case-based training and practical scenarios designed to guide them through the interview processes at institutions including the University of Toronto and Western University, to name a few.
Remember:
Regardless of whichever route you choose, becoming a dentist in Canada is a huge commitment, both financially and in the amount of time needed (find out about financing options here). Always feel free to reach out to the school or institution of your choice to learn more information and weigh your options.
To help give you the best information to make an informed decision, Prep Doctors offers scheduled tours of our campus and facilities, as well as demo classes and financial counselling. Our team is always available to answer any questions about the dental equivalency journey. So, please reach out to us through our Facebook page or email us at info@prepdoctors.ca. We are more than happy to help!

